Overview: Achieving 94.7% accuracy on English tense classification required careful model selection and training strategies specifically designed for Thai learners' common grammatical errors. This post explores the development of a hierarchical 24-category classification system that forms the heart of Thaislate's educational intelligence.
The Critical Need for Specialized Tense Classification
The development of a dedicated tense classification model emerged from a fundamental limitation discovered during system testing: general-purpose language models consistently failed at accurate tense identification, which would have undermined the entire educational purpose of the system.
The Discovery That Changed Everything
Initial experiments with GPT-style instruction-following models seemed potentially viable as they could handle translation and explanation generation reasonably well. However, when tasked with tense classification, these models demonstrated concerning inconsistency.
A sentence like "I have been studying for three years" might be classified as "Present Continuous" on one attempt and "Present Perfect Continuous" on another, despite being identical input. This unpredictability would be pedagogically harmful, as learners could receive conflicting explanations for the same grammatical structure.
Unlike general NLP applications where small classification errors might be acceptable, educational systems require high reliability. An incorrect tense classification leads directly to incorrect grammar explanation, potentially reinforcing learner errors rather than correcting them. For Thai learners already struggling with English temporal concepts, such misinformation could significantly impede learning progress.
Design Requirements for Educational Reliability
This discovery necessitated developing a classification system optimized specifically for educational reliability:
Core Requirements
- Consistency: Identical inputs must produce identical classifications every time
- Nuanced Distinction: Ability to distinguish between subtle tense variations crucial for Thai learners (e.g., habits vs. general facts)
- Confidence Scoring: Quantified certainty levels to identify potentially problematic classifications
- Educational Taxonomy: Classification categories aligned with how tenses are taught to Thai learners
The 24-Category Tense Taxonomy
The classification system implements a custom taxonomy developed with reference to established Thai grammar teaching materials, designed to address specific challenges Thai learners face:
Present Tenses (9 categories)
Perfect Tenses (4 categories)
Past Tenses (5 categories)
Future Tenses (6 categories)
Dataset Preparation and Curation
The classification model was trained on a carefully curated dataset combining multiple sources to ensure comprehensive coverage of English tense structures:
Dataset Composition

Manual Annotation Process
The 2,505 fine-grained labels were manually annotated by analyzing each sentence for its primary tense usage pattern and labeling according to the 24-category taxonomy framework. Labels were assigned based on Thai teaching methodology and learning objectives, with ambiguous cases resolved using context and primary grammatical intent.
Ethical Considerations
The dataset annotation process received separate ethical approval from the University Research Ethics Committee of the University of Sheffield (Application Number 070793). All sentences came from publicly available Kaggle datasets and contained no personally identifiable information.
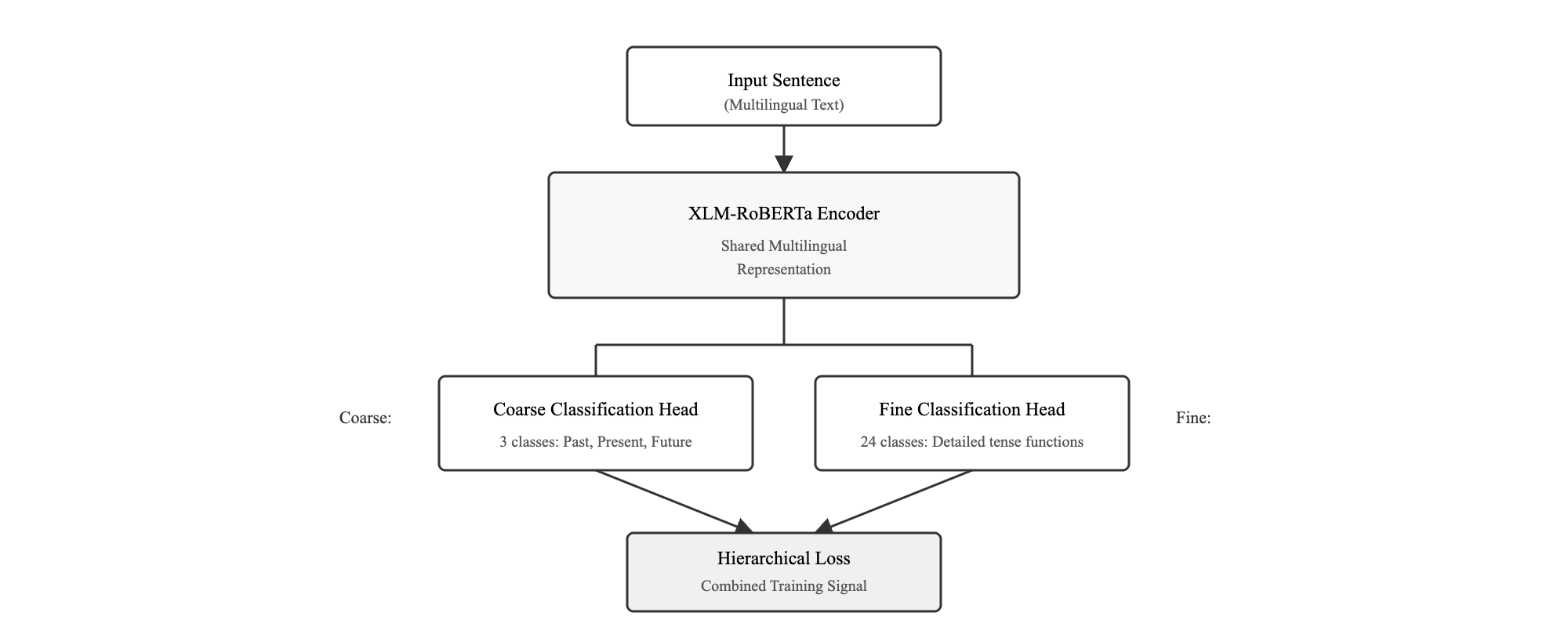
Hierarchical Classification Architecture
The core innovation of the tense classification system lies in its hierarchical approach, which mirrors how humans naturally understand temporal relationships by first identifying the broad time frame (past, present, future) before determining specific grammatical functions.

Dual-Head Architecture
The model employs a dual-head architecture where XLM-RoBERTa's multilingual encoder feeds into two classification heads:
Coarse Head
Predicts broad temporal categories (Past/Present/Future) - provides foundational temporal understanding and fallback capability
Fine Head
Predicts specific tense functions (24 detailed categories) - enables precise grammatical instruction for educational purposes
Shared Encoder
XLM-RoBERTa processes multilingual input understanding - leverages cross-lingual knowledge for Thai-English contexts
Training Strategy and Loss Optimization
The model uses weighted loss optimization that balances both classification levels to ensure both temporal consistency and detailed grammatical accuracy:
Weighted Loss Distribution
- 70% weight on fine-grained accuracy: Prioritizes the detailed classifications needed for grammar instruction
- 30% weight on coarse accuracy: Ensures temporal consistency and provides fallback capability
- Combined loss function: Prevents the model from achieving fine-grained accuracy at the expense of basic temporal understanding
Hierarchical Approach Benefits
- Pedagogical Alignment: Matches how tenses are taught with broad concepts first, then specific applications
- Error Mitigation: If fine-grained classification fails, coarse classification can still provide useful educational feedback
- Training Efficiency: Shared temporal knowledge improves learning across related categories
Performance Results
The specialized classification system demonstrates significant improvements over general-purpose models:
Classification Performance
XLM-RoBERTa: The Foundation
The choice of XLM-RoBERTa as the base model provides several advantages for Thai-English educational contexts:
- Multilingual Understanding: Pre-trained on 100 languages including Thai and English
- Cross-lingual Transfer: Leverages knowledge from related languages and structures
- Robust Performance: Demonstrated state-of-the-art results in cross-lingual classification tasks
- Educational Suitability: Balanced model size suitable for educational deployment
Key Innovation: Educational vs. Technical Performance
The Insight That Matters
The difference between isolated accuracy (94.7%) and pipeline accuracy (74%) revealed a crucial insight: while technical degradation occurs in real-world deployment, user satisfaction remained high (4.33/5 for explanation quality).
This demonstrates that educational effectiveness isn't purely determined by technical metrics—learners value clear, consistent explanations even when the underlying classification isn't perfect.
Impact on Educational AI
The hierarchical BERT classifier represents a significant contribution to educational natural language processing:
- Specialized Taxonomy: First implementation of Thai learner-specific English tense categories
- Hierarchical Design: Novel dual-head architecture for educational classification
- Consistency Achievement: Reliable performance crucial for educational applications
- Cross-linguistic Bridge: Effective handling of Thai-English grammatical differences
Continue the Technical Journey
Explore more aspects of the system: